
When it comes to understanding the mechanics of vehicles, one of the fundamental aspects to consider is the suspension system. This system plays a critical role in determining a vehicle’s handling, ride quality, and overall performance. In the realm of suspension systems, the distinctions between 2WD (two-wheel drive) and 4WD (four-wheel drive) setups are particularly important for drivers who seek specific advantages based on their driving conditions and needs.
The main difference between 2WD and 4WD suspension systems lies in how they distribute power to the wheels. A 2WD system powers only one set of wheels, which can contribute to a lighter and simpler suspension design. This can result in better fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance. Conversely, a 4WD system powers all four wheels, which enhances traction and control, particularly in off-road or adverse weather conditions.
Moreover, the configurations of their respective suspension systems directly affect ride comfort and handling dynamics. 2WD vehicles often use designs optimized for on-road driving, which may compromise off-road capabilities. In contrast, 4WD systems are engineered for versatility, providing enhanced stability and performance across various terrains. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone looking to choose the right vehicle for their lifestyle and driving environment.
Impact of Drive System on Suspension Design
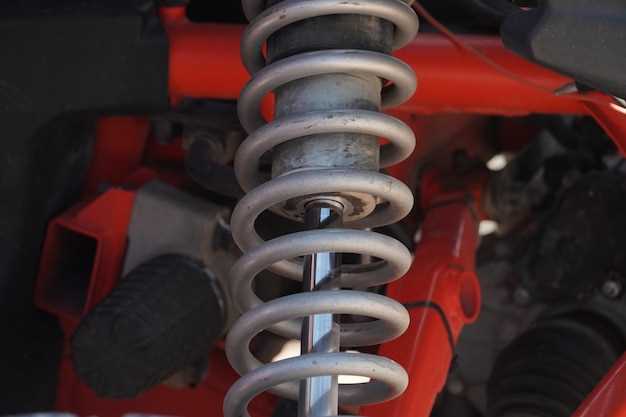

The drive system of a vehicle significantly influences its suspension design, particularly when comparing two-wheel drive (2WD) and four-wheel drive (4WD) configurations. The key differences in power delivery and vehicle dynamics necessitate distinct engineering approaches in the suspension systems of these vehicles.
In 2WD vehicles, the suspension is optimized primarily for efficient handling and ride comfort since only two wheels receive power. This allows for lighter components and a focus on maintaining optimal stability during acceleration and braking. The design can prioritize features such as softer spring rates and shock absorbers tailored for everyday driving conditions, enhancing passenger comfort on paved surfaces.
Conversely, 4WD systems demand a more robust suspension design to handle the additional stresses associated with off-road conditions and uneven terrain. The need for improved traction and stability across all four wheels requires stiffer springs and advanced dampers. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate challenging environments while maintaining control and comfort, even under heavy loads or rough surfaces.
Furthermore, the integration of the driveline into the suspension system in 4WD vehicles often necessitates unique geometries to accommodate various drivetrain components. This may lead to a more complex architecture involving multi-link systems or independent suspensions that allow for better wheel articulation and ground contact while driving over obstacles.
In addition to structural differences, the weight distribution between 2WD and 4WD systems also plays a crucial role in suspension tuning. 4WD vehicles typically carry more weight due to additional components like transfer cases and differentials, which can influence the overall balance and handling characteristics. This requires careful calibration of suspension settings to ensure stability and responsiveness across varying driving scenarios.
Overall, the choice of drive system fundamentally shapes the design priorities and configurations of suspension systems, dictating factors such as component durability, weight, and ride quality. Understanding these impacts is essential for manufacturers and consumers alike when evaluating vehicle performance and suitability for specific driving environments.
How Terrain Affects 2WD and 4WD Suspension Performance

The performance of 2WD and 4WD suspension systems is significantly influenced by the terrain on which the vehicle is operated. In general, 2WD systems excel in flat, paved conditions, where traction is consistent and predictable. On smooth surfaces, the suspension setup is optimized for comfort and stability, allowing for a smooth ride without excessive body roll.
However, when navigating uneven or rugged terrains, the limitations of 2WD systems become apparent. The lack of drive in the rear wheels can lead to reduced traction on loose surfaces, such as gravel, mud, or sand. The suspension may struggle to maintain optimal contact with the ground, resulting in a rougher ride and decreased handling stability.
In contrast, 4WD systems are designed for versatility and off-road capabilities. Their suspension systems are engineered to handle a wide range of terrains, providing better ground clearance and articulation. When encountering obstacles like rocks or steep inclines, 4WD allows for power distribution to all four wheels, enhancing grip and traction. This capability enables the suspension to adapt more effectively to sudden changes in terrain, improving performance and driver confidence.
Additionally, 4WD suspensions often come equipped with features such as locking differentials and adjustable ride height, further enhancing their ability to tackle challenging environments. The dual focus on both comfort and ruggedness results in a system that maintains productivity across various conditions.
In summary, while 2WD systems are suitable for everyday driving on smooth roads, their performance can diminish in diverse terrains. In contrast, 4WD systems provide greater adaptability and control, making them the preferred choice for off-road driving and challenging landscapes.
Maintenance Considerations for 2WD vs 4WD Suspensions
Maintaining a suspension system is critical for ensuring optimal performance and safety, whether in a 2WD or 4WD vehicle. However, differences in design and functionality lead to distinct maintenance requirements for both systems.
2WD suspensions generally have fewer components than 4WD systems, which can simplify maintenance. Owners of 2WD vehicles may focus primarily on routine checks of shock absorbers, springs, and bushings. Since these vehicles primarily operate in a two-wheel configuration, wear and tear on the suspension components are often less pronounced, making periodic inspections less intensive.
In contrast, 4WD suspensions involve additional elements such as transfer cases, front differentials, and a more complex arrangement of links and joints. This complexity means that maintenance can be more labor-intensive. Regular inspections are necessary to check for lubrication needs, particularly in joints that are involved in engaging and disengaging the 4WD system. Neglecting these components can result in costly repairs down the line.
Another key difference lies in the type of driving conditions these vehicles typically face. 4WD vehicles are often subjected to off-road conditions that can rapidly accelerate wear on suspension parts. Dust, mud, and rocks can lead to increased friction and potential damage, making regular cleaning and lubrication essential. Conversely, 2WD vehicles are usually driven on paved roads, where environmental factors are less abrasive, potentially reducing the frequency of maintenance needs.
Additionally, shock absorbers in 4WD vehicles may require more frequent replacement due to the increased stress placed on them during off-road excursions. They should be checked regularly for leaks or signs of wear to ensure proper handling and ride comfort. In both systems, bushings and ball joints should be examined for deterioration, as a compromised joint can affect overall suspension performance.
In summary, while both 2WD and 4WD suspensions require routine maintenance, the complexity and driving conditions associated with 4WD systems necessitate more frequent inspections and potentially more comprehensive care. Understanding these differences can help vehicle owners make informed decisions about their maintenance routines.






