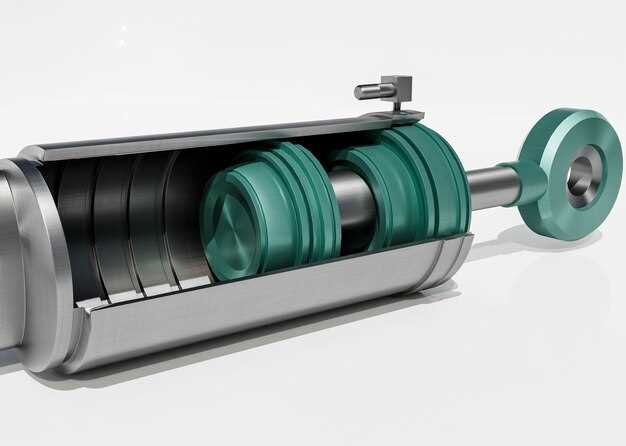


Torque converters are a fundamental component in automatic transmission systems, playing a pivotal role in a vehicle’s motion dynamics. By transferring power from the engine to the transmission, the converter allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration, significantly influencing the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle. The unique design of a torque converter, which utilizes fluid dynamics to transfer torque, distinguishes it from other types of coupling mechanisms.
One of the primary functions of a torque converter is to multiply the engine’s torque under specific conditions, allowing for enhanced vehicle responsiveness. This characteristic is especially crucial during initial acceleration when torque demand is high. The behavior of the torque converter affects not only how quickly a vehicle can accelerate but also how efficiently it operates under various driving conditions, including stop-and-go traffic and highway cruising.
Moreover, the impact of a torque converter extends to vehicle stability and control. With its ability to provide a variable level of torque multiplication based on engine speed and load, the converter can help manage power delivery in relation to the vehicle’s velocity. Understanding the intricacies of torque converters and their influence on motion dynamics is essential for optimizing vehicle design and enhancing driver experience.
Torque Converter Role in Drivetrain Functionality
A torque converter is an essential component in automatic transmissions that facilitates the transfer of torque from the engine to the drivetrain. By using a fluid coupling mechanism, it allows for a smooth and efficient transfer of power, significantly enhancing vehicle motion dynamics.
The fundamental role of a torque converter is to multiply engine torque during initial acceleration, which provides the necessary force to move the vehicle. This is particularly important when starting from a stop, as it enables the driver to accelerate smoothly without stalling the engine. The converter achieves this by using a turbine and a stator, which work in harmony to increase the torque output at low speeds.
In addition to torque multiplication, a torque converter also serves as a hydraulic damper. It absorbs rotational fluctuations from the engine, reducing vibrations and contributing to a more stable driving experience. This damping effect is crucial during transitions between different driving conditions, such as accelerating, decelerating, or climbing hills.
The efficiency of the torque converter significantly impacts overall drivetrain functionality. Modern torque converters often incorporate lock-up mechanisms, which allow for a direct connection between the engine and transmission at higher speeds. This feature minimizes power loss due to slippage and increases fuel efficiency, thereby enhancing vehicle performance.
Furthermore, the design of the torque converter affects shifting characteristics within the automatic transmission. By providing a variable transmission ratio, it allows for smoother gear changes and better responsiveness, which improves driver control and vehicle handling.
In summary, the torque converter plays a critical role in the drivetrain by facilitating torque multiplication, providing hydraulic damping, and enhancing overall efficiency. Its contribution to vehicle motion dynamics is vital for achieving optimal performance and driver satisfaction.
Effects of Torque Converter Lock-Up on Acceleration and Fuel Economy
The torque converter is a critical component of an automatic transmission system, serving to transmit power from the engine to the drivetrain. One of its key features is the lock-up function, which becomes active during specific driving conditions. This feature has significant implications for both acceleration and fuel economy.
Acceleration Performance: When the torque converter engages the lock-up mode, it creates a mechanical connection between the engine and the drivetrain. This eliminates the slip inherent in traditional torque converters, allowing for more direct power transfer. As a result, vehicles experience improved acceleration since the engine’s power reaches the wheels more effectively. The reduction in engine RPMs during lock-up means that there is less energy loss, making acceleration more responsive and efficient.
Fuel Economy Benefits: The lock-up feature plays a pivotal role in enhancing fuel efficiency as well. By minimizing the slippage of the converter, a vehicle can maintain a lower engine speed at cruising conditions. This reduction in RPM leads to decreased fuel consumption, as the engine operates more within its optimal efficiency range. Consequently, vehicles with a well-functioning torque converter lock-up tend to exhibit better fuel economy, especially during highway driving where constant speeds are maintained.
In summary, the lock-up function of a torque converter significantly influences both acceleration and fuel efficiency. By providing a direct connection between the engine and the drivetrain, it enhances vehicle performance and minimizes energy loss, resulting in a more economical driving experience.
Comparison of Torque Converter Types and Their Influence on Handling
The drivetrain of a vehicle plays a critical role in its overall performance, and the type of converter used can significantly affect handling characteristics. Torque converters are typically classified into three main types: traditional hydraulic, lock-up, and variable geometry. Each type has its own unique influence on vehicle dynamics.
Traditional hydraulic torque converters utilize fluid coupling to transmit power from the engine to the transmission. This design allows for smooth acceleration and efficient power transfer, but it can introduce delays in response time during rapid changes in throttle input. Consequently, vehicles equipped with this type of converter may experience a sensation of lag during sharp maneuvers, negatively impacting handling precision.
The lock-up torque converter addresses some of the inefficiencies of traditional systems by engaging a mechanical lock-up clutch at higher speeds. This direct connection between the engine and drivetrain minimizes slip, leading to improved fuel efficiency and more immediate power delivery. As a result, vehicle handling is enhanced, particularly during high-speed cornering, where responsiveness is crucial.
Variable geometry torque converters represent the latest advancement in converter technology, featuring adjustable blade designs that optimize performance based on driving conditions. By altering the fluid dynamics within the converter, these systems can provide immediate torque delivery and improved engine responsiveness. Vehicles utilizing variable geometry converters generally exhibit superior handling characteristics, achieving better stability and agility in various driving scenarios.
In summary, the choice of torque converter has a profound impact on a vehicle’s handling dynamics. Traditional hydraulic converters may provide a comfortable driving experience but can compromise responsiveness, while lock-up converters enhance efficiency and directness. Variable geometry designs push the boundaries of handling performance, making them an ideal choice for enthusiasts seeking precision in their vehicles.







